Understanding Recurrent Pneumothorax Treatment: An In-Depth Exploration
Recurrent pneumothorax is a condition characterized by the repeated presence of air in the pleural space, leading to lung collapse. This article aims to provide a thorough understanding of the treatment options available for this condition, the underlying causes, and the importance of seeking specialized care from experienced professionals.
What is Pneumothorax?
Pneumothorax, commonly referred to as a collapsed lung, occurs when air leaks into the pleural space—the area between the lung and the chest wall. This can lead to discomfort, chest pain, shortness of breath, and, in severe cases, respiratory failure.
Causes of Recurrent Pneumothorax
Several factors can contribute to the recurrence of pneumothorax, including:
- Spontaneous Pneumothorax: Often seen in tall, young males and can occur without obvious injury.
- Traumatic Pneumothorax: Resulting from blunt or penetrating chest trauma.
- Underlying Lung Conditions: Such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, or cystic fibrosis.
- Structural Lung Defects: Conditions like blebs or bullae that may rupture spontaneously.
Symptoms of Recurrent Pneumothorax
Individuals suffering from recurrent pneumothorax may experience a range of symptoms, which include:
- Chest Pain: Sharp or stabbing pain that intensifies with breath.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, especially during exertion.
- Coughing: Coughing that may produce blood or be accompanied by wheezing.
- Fast Heart Rate: Increased heart rate due to decreased oxygen levels.
The Importance of Consultation
Consulting healthcare professionals at specialized medical centers, such as Neumark Surgery, is crucial for individuals with a history of pneumothorax. A multidisciplinary approach ensures optimum treatment tailored to the patient's specific needs.
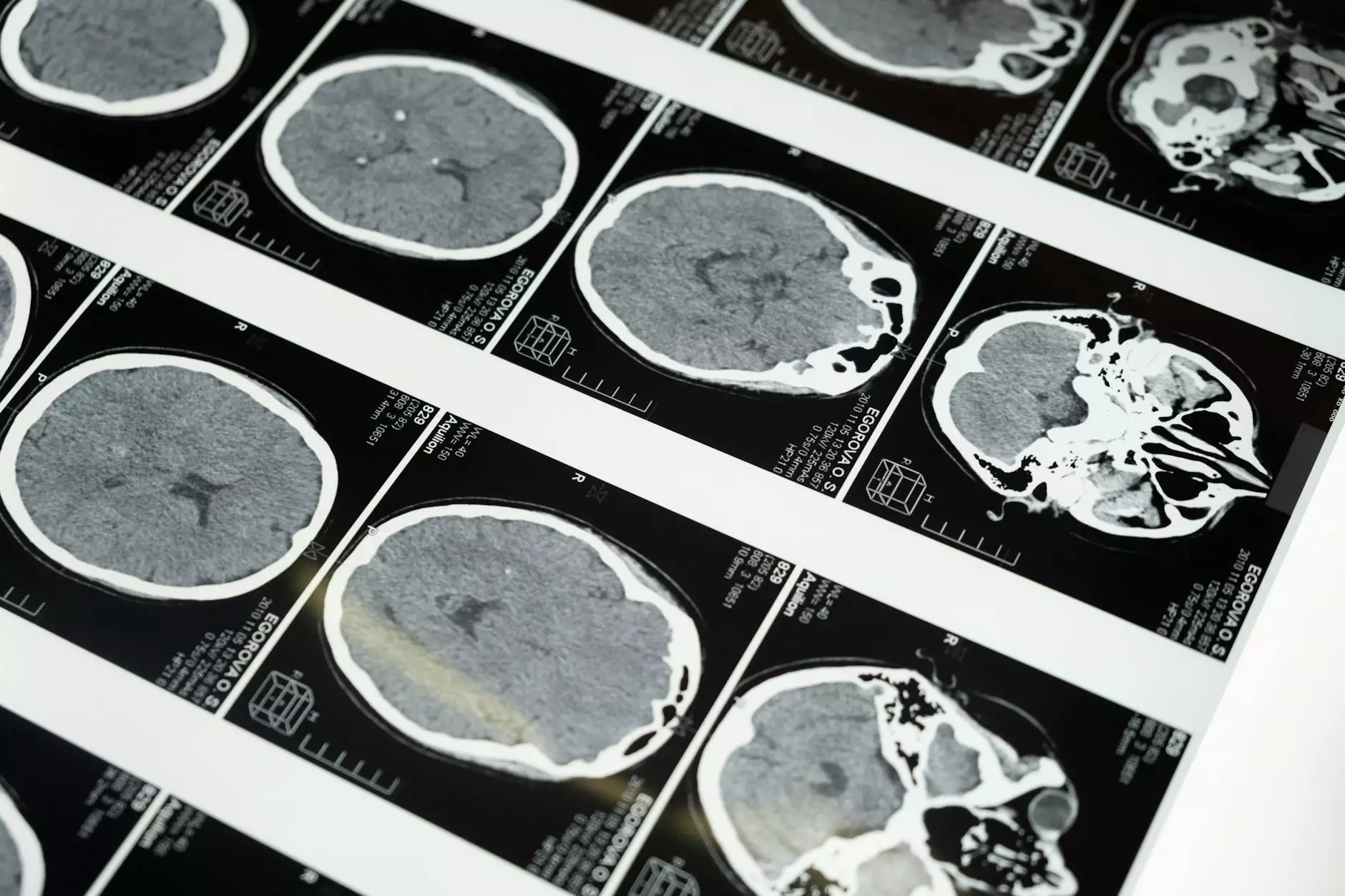
Diagnosis of Pneumothorax
The diagnosis of recurrent pneumothorax usually involves:
- Physical Examination: Assessment of lung sounds, breathing patterns, and chest movement.
- Radiologic Imaging: Chest X-rays and CT scans help visualize the extent of lung collapse.
- Oxygen Saturation Monitoring: Non-invasive testing to measure the oxygen levels in the blood.
Recurrent Pneumothorax Treatment Options
Treatment for recurrent pneumothorax aims to relieve symptoms, prevent recurrences, and address underlying causes. Several treatment options are available, depending on the severity and frequency of episodes.
1. Observation and Supportive Care
If the pneumothorax is small and not causing significant symptoms, a conservative approach may be adopted. This involves:
- Monitoring: Regular follow-up appointments to assess lung function.
- Pain Management: Use of over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Oxygen Therapy: Supplemental oxygen may help in resolution.
2. Needle Decompression
For a larger pneumothorax, a medical professional may perform needle decompression, a procedure that involves:
- Inserting a Needle: A hollow needle is inserted into the pleural space to extract air.
- Temporary Relief: This is a quick method to alleviate pressure on the lung.
3. Chest Tube Insertion
In cases where a needle decompression is insufficient, a chest tube may be inserted. This involves:
- Suctioning Air: The tube allows continuous drainage of air from the pleural space.
- Monitoring: Patients will be monitored closely during this process.
4. Surgical Intervention
For patients with recurrent pneumothorax who do not respond to conservative treatments, surgery may be required. Surgical options include:
- Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS): Minimally invasive procedure to repair the lung and remove blebs or bullae.
- Pleurodesis: A procedure that adheres the lung to the chest wall to prevent future pneumothorax.
Post-Treatment Care and Rehabilitation
After treatment for recurrent pneumothorax, follow-up care is critically important. Considerations include:
- Regular Check-Ups: To ensure lung recovery and monitor for recurrence.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: Breathing exercises and physical therapy as needed.
- Avoiding Risk Factors: Patients should be educated about avoiding activities that may increase the risk of recurrence.
Living with Recurrent Pneumothorax
Living with the threat of recurrent pneumothorax can be challenging, but managing one’s lifestyle plays a significant role in treatment outcomes. Tips for daily management include:
- Staying Active: Regular, gentle exercise can improve lung function.
- Avoiding Smoking: Smoking cessation is crucial for lung health.
- Monitoring Symptoms: Keeping an eye on any worsening symptoms or new developments.
- Seeking Immediate Care: Understanding when to seek help if symptoms return.
Conclusion
Recurrent pneumothorax treatment involves a comprehensive approach that includes diagnosis, individualized treatment plans, and close follow-up. By collaborating with skilled professionals at centers like Neumark Surgery, patients can ensure they receive the most effective management for their condition. If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms of pneumothorax, do not hesitate to seek specialized medical attention to achieve the best possible outcomes.
Investing in your lung health is vital. Always prioritize seeking professional care, early intervention, and support from healthcare providers.
recurrent pneumothorax treatment